Life insurance plans are essential financial tools that provide a safety net for your loved ones. Understanding the various types, associated costs, and benefits is crucial for making informed decisions.
This guide delves into the intricacies of life insurance, from the fundamental concepts to specific considerations for different life stages and needs. We explore different types of plans, examining their features, benefits, and limitations. The cost of life insurance is also discussed, highlighting factors that affect premiums. Ultimately, this guide aims to empower you to make the best choice for your financial security.
Introduction to Life Insurance Plans
Life insurance plans are financial products designed to provide a death benefit to beneficiaries upon the insured’s demise. These plans offer a safety net for loved ones, ensuring financial security in the event of unforeseen circumstances. They also play a vital role in estate planning and long-term financial security.Different life insurance plans cater to various needs and risk tolerances.
Some plans focus on providing a lump sum payment, while others offer a combination of death benefits and cash value accumulation. Understanding the nuances of different plans is crucial for making informed decisions.
Defining Life Insurance Plans
Life insurance plans are contracts between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company (the insurer). These contracts promise a payout (the death benefit) to designated beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s death. This payout acts as financial support for dependents or other beneficiaries.
Purposes of Life Insurance Plans
Life insurance plans serve several important purposes. Primarily, they provide a financial safety net for loved ones by covering potential financial losses in the event of the policyholder’s death. Secondly, they can be used for estate planning, enabling individuals to transfer assets to beneficiaries. Thirdly, some plans offer cash value accumulation, allowing for savings and investment opportunities.
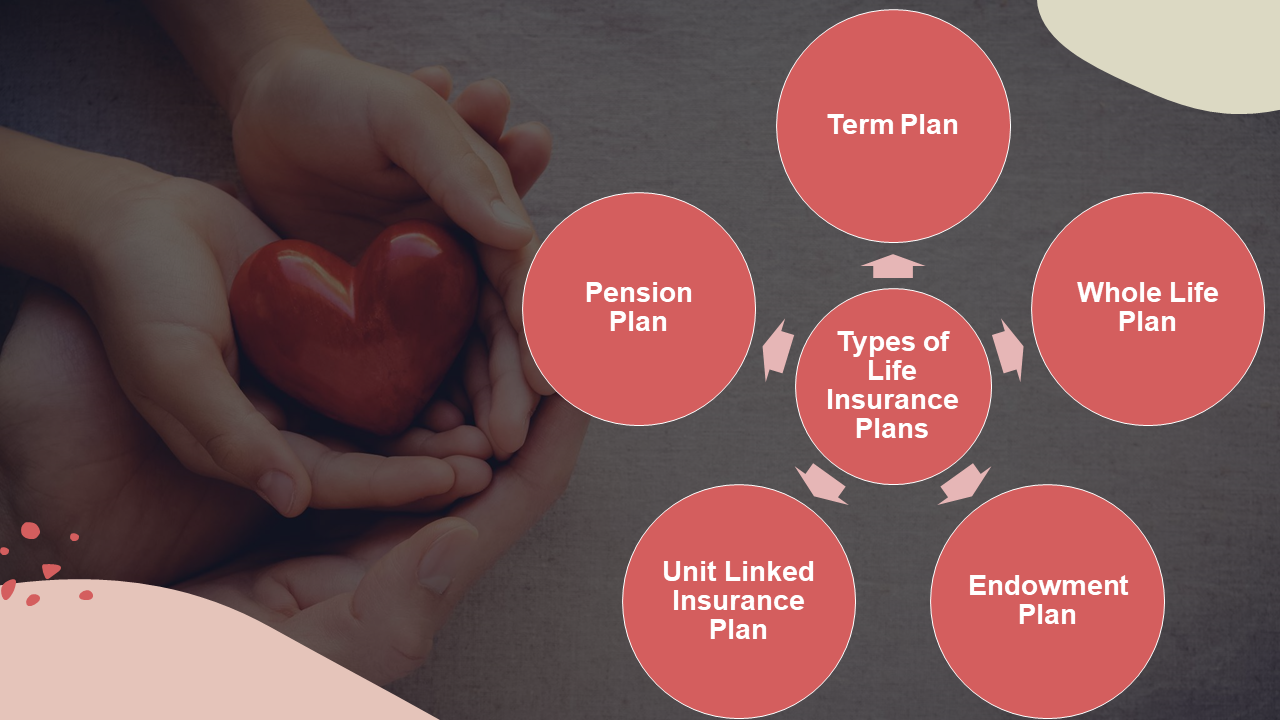
Types of Life Insurance Plans
Several types of life insurance plans exist, each with unique features and benefits. These include term life insurance, whole life insurance, and universal life insurance.
Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period (term). If the insured dies during the term, beneficiaries receive a death benefit. Premiums are typically lower than other types of plans, making them an attractive option for those seeking temporary coverage. The coverage ends at the end of the term. Key components include the term length, death benefit amount, and premium.
Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage. Premiums remain constant throughout the policy’s duration. A portion of the premiums is invested, potentially building cash value over time. This cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn, depending on the plan’s provisions. Key components include the death benefit, premiums, cash value accumulation, and policy dividends.
Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance offers lifelong coverage, similar to whole life. However, premiums and death benefits are flexible. The policyholder can adjust premiums and death benefits as needed. A portion of the premiums is invested, with the potential for higher returns compared to whole life. Key components include the death benefit, premiums, and investment options.
Comparison of Life Insurance Plans
| Plan Type | Premiums | Coverage Amounts | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Term Life | Lower | Specified term | Temporary coverage; often affordable |
| Whole Life | Constant | Lifelong | Cash value accumulation; policy dividends |
| Universal Life | Flexible | Lifelong | Adjustments possible; potentially higher returns |
Factors Affecting Life Insurance Premiums
Life insurance premiums are not a fixed amount; they are calculated based on various factors that assess the risk associated with insuring a particular individual. Understanding these factors is crucial for prospective policyholders to make informed decisions about the appropriate coverage and cost. These factors play a significant role in determining the financial commitment involved in securing life insurance protection.
Age
Age is a primary determinant of life insurance premiums. Younger individuals are generally considered lower risk due to their longer life expectancy, and thus, premiums are lower. Conversely, older individuals have a shorter expected lifespan and a higher probability of mortality, leading to higher premiums. This is a direct reflection of the actuarial data used to assess risk.
For instance, a 25-year-old with good health will likely pay a lower premium compared to a 65-year-old with similar health.
Health
Health conditions significantly influence premium costs. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer, are often assessed as higher risk and face higher premiums. Conversely, individuals with excellent health and a history of regular check-ups and healthy habits will likely have lower premiums. A person with a history of frequent hospitalizations will have a different premium compared to someone with a clean medical history.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle choices also play a role in premium calculations. Activities like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a lack of physical activity increase the risk of premature death, leading to higher premiums. Individuals who maintain a healthy lifestyle, engage in regular exercise, and have a balanced diet often qualify for lower premiums. A smoker will likely pay a much higher premium compared to a non-smoker with similar age and health.
Occupation
Certain occupations carry a higher risk of death or injury, leading to higher premiums. For example, individuals in high-risk professions like firefighters, police officers, or construction workers may pay more compared to office workers or teachers. Hazardous occupations require higher premiums due to increased mortality risks associated with their work.
Coverage Amount
The amount of coverage requested directly affects the premium. A larger coverage amount generally results in a higher premium due to the increased financial responsibility for the insurance company. The amount of coverage required must be carefully considered alongside the premium costs to ensure affordability. Higher coverage means a greater financial commitment for the insurance provider.
Examples of Premium Variations
- A 30-year-old nonsmoker with no pre-existing conditions will have lower premiums compared to a 60-year-old smoker with a history of heart disease.
- An individual in a high-risk occupation like a professional race car driver will pay more than a teacher.
- Requesting a larger coverage amount will increase the premium.
Factors Affecting Premiums and Potential Impact
| Factor | Potential Impact on Policy Costs |
|---|---|
| Age | Higher age generally leads to higher premiums. |
| Health | Pre-existing conditions or poor health increase premiums. |
| Lifestyle | Unhealthy habits (smoking, excessive drinking) result in higher premiums. |
| Occupation | High-risk occupations typically have higher premiums. |
| Coverage Amount | Larger coverage amounts increase premiums. |
Benefits and Advantages of Life Insurance Plans
Life insurance plans offer a range of financial benefits that can protect individuals and families from unforeseen circumstances. These plans provide a safety net, offering peace of mind and ensuring financial security for loved ones in the event of a life-altering event. Understanding the advantages of life insurance is crucial for making informed decisions about your financial well-being.Life insurance policies provide a significant financial cushion, enabling beneficiaries to manage expenses and maintain their lifestyle without undue hardship.
The benefits extend beyond simple monetary compensation; they often facilitate the smooth transition during a period of significant loss and offer the chance for a more secure future.
Financial Benefits of Life Insurance
Life insurance policies offer substantial financial support to beneficiaries, enabling them to cover various expenses. The death benefit, a crucial component of most policies, is a lump-sum payment made to the designated beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s demise. This payment can be used for funeral expenses, outstanding debts, educational funds, or to maintain the family’s standard of living. A common example is a young family where the primary breadwinner unexpectedly passes away; the death benefit can provide the necessary funds to cover mortgage payments, children’s education, and daily living expenses, alleviating the family’s immediate financial burden.
Advantages for Individuals and Families
Life insurance offers significant advantages for both individuals and families. For individuals, it serves as a financial safety net, safeguarding their loved ones’ financial well-being in case of their untimely demise. The death benefit ensures that beneficiaries can maintain their current lifestyle without experiencing a significant financial setback. For families, life insurance is a crucial tool for estate planning and protecting their future.
It allows the family to continue operating as a unit, with the financial resources needed to transition into the next phase.
Life Insurance and Estate Planning
Life insurance plays a critical role in estate planning. The death benefit can be utilized to settle outstanding debts, fund inheritances, and cover estate taxes, simplifying the estate administration process for the beneficiaries. It helps ensure that assets are distributed according to the policyholder’s wishes and that the family’s financial future remains secure. In many cases, a properly structured life insurance policy can significantly reduce the tax burden on the estate.
Coverage for Unforeseen Events
While primarily designed for death benefits, life insurance policies can sometimes offer coverage for unforeseen events, such as critical illness or accidental death. Certain policies include riders that extend coverage beyond the standard death benefit, offering additional financial support during challenging times. This flexibility provides a more comprehensive safety net for individuals and families, ensuring financial protection in various life circumstances.
Tax Implications of Life Insurance
The tax implications of life insurance vary depending on the type of policy and the specific circumstances. Generally, the death benefit received by beneficiaries is tax-free. However, certain policy premiums may be tax-deductible, depending on the individual’s tax bracket and specific policy terms. Consulting a tax advisor is crucial to understanding the specific tax implications of a life insurance policy in relation to an individual’s circumstances.
Financial Security Provided by Life Insurance
Life insurance plans offer multiple avenues for achieving financial security.
- Debt Repayment: The death benefit can be used to repay outstanding debts, including mortgages, loans, and credit card balances, protecting the beneficiaries from these obligations.
- Funeral Expenses: A life insurance policy can cover funeral expenses, ensuring that the deceased’s final arrangements are handled without adding financial strain to the family.
- Education Funding: The death benefit can provide funds for the education of children or dependents, ensuring their future educational aspirations are met.
- Income Replacement: For individuals who are the primary breadwinners, the death benefit can provide a source of income to replace lost earnings and support dependents.
- Estate Settlement: Life insurance can facilitate the smooth settlement of an estate, minimizing complications and ensuring that assets are distributed according to the deceased’s wishes.
Choosing the Right Life Insurance Plan
Selecting the appropriate life insurance policy is a crucial financial decision. It requires careful consideration of your personal circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. Understanding the different types of policies and their features is essential to making an informed choice. A well-chosen plan can provide significant protection for your loved ones and contribute to long-term financial security.
Steps in Selecting a Life Insurance Policy
Thorough research and a methodical approach are key to finding the right life insurance policy. This involves understanding your specific needs, evaluating different policy options, and making a well-informed decision. A proactive approach ensures the chosen policy aligns with your current and future financial goals.
- Assess your financial needs and goals: Consider your current income, outstanding debts, and future financial obligations, such as education expenses for children or retirement planning. Understanding your financial situation is critical for determining the appropriate coverage amount.
- Evaluate different types of life insurance policies: Explore term life insurance, permanent life insurance (whole life, universal life, variable life), and other available options. Each type offers distinct benefits and features, tailored to varying financial situations and needs.
- Compare policy features and premiums: Carefully examine policy features, including coverage amounts, premiums, policy terms, and any riders. Comparing different policies side-by-side can provide a clear understanding of the cost-benefit ratio of each option.
- Consider your risk tolerance: Evaluate your comfort level with different insurance options. This includes understanding the risks associated with each type of policy and the financial implications of those risks. A comprehensive understanding of the risks and rewards is crucial.
- Seek professional advice: Consulting with a financial advisor is highly recommended. A financial advisor can provide personalized guidance, ensuring the chosen policy aligns with your individual circumstances and financial goals. Their expertise can prevent potential pitfalls and ensure a well-informed decision.
Comparing Different Life Insurance Policies
Comparing policies involves a meticulous evaluation of their terms and conditions, and not just focusing on the premium. This process helps ensure the chosen policy offers the best possible value.
| Feature | Term Life Insurance | Permanent Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Period | Specific time period (e.g., 10, 20, 30 years) | Lifetime |
| Premium | Typically lower | Typically higher |
| Cash Value | No cash value component | Accumulates cash value |
| Flexibility | Relatively flexible | Less flexible |
Careful comparison of features, including coverage amounts, premiums, policy terms, and riders, is essential. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each type of policy is crucial for making an informed decision.
Considering Individual Needs and Financial Goals
A suitable life insurance policy should reflect your specific circumstances and future goals. A well-defined understanding of your financial situation and future aspirations is crucial for choosing the right coverage.
- Family size and responsibilities: The number of dependents and their financial needs influence the necessary coverage amount. A family with young children might require a higher coverage amount than a single individual.
- Outstanding debts: The existence and amount of outstanding debts, such as mortgages or student loans, affect the required coverage amount. This is because the coverage should ideally surpass the debts to provide sufficient funds for dependents.
- Future financial goals: Considerations such as education expenses for children or retirement planning should be factored into the coverage amount. This ensures the chosen coverage amount aligns with future aspirations.
Importance of Consulting with a Financial Advisor
A financial advisor provides personalized guidance and helps in navigating the complexities of life insurance policies. Their expertise is invaluable in ensuring the chosen policy aligns with individual circumstances.
Seeking professional advice is highly recommended to avoid making costly mistakes.
A financial advisor’s expertise can help tailor the policy to specific needs, ensuring the chosen policy is the most suitable option for your circumstances.
Step-by-Step Guide for Selecting a Life Insurance Plan
A structured approach is essential to choosing the right life insurance plan.
- Define your financial needs and goals.
- Research different types of life insurance policies.
- Compare policy features, premiums, and coverage amounts.
- Evaluate your risk tolerance and personal circumstances.
- Seek professional advice from a financial advisor.
- Make a well-informed decision based on your needs and goals.
Understanding Life Insurance Policies
Life insurance policies are legally binding contracts. They Artikel the terms and conditions of the agreement between the policyholder and the insurance company. Thorough understanding of these documents is crucial for both policyholders and beneficiaries to ensure clarity and avoid potential disputes. Navigating these policies can seem daunting, but a structured approach makes the process manageable.
Policy Document Overview
Life insurance policies are comprehensive documents detailing the agreement between the policyholder and the insurance company. These documents typically include detailed information about the insured, the coverage amount, payment terms, and the benefits payable in the event of a covered loss. The policy also specifies exclusions and limitations to the coverage. This detailed information is crucial for both parties involved to understand the responsibilities and expectations.
Key Terms and Conditions
The policy document lays out the terms and conditions, defining the parameters of the agreement. These terms encompass essential elements like the policy’s duration, the premium payment schedule, and the specific circumstances under which the insurance company is obligated to pay benefits. It also includes details on how the policy can be amended or terminated. Comprehending these details is vital for policyholders to manage their financial obligations and beneficiaries to understand their rights.
Key Clauses and Provisions
Various clauses and provisions form the core of the policy, outlining the specifics of the agreement. These include the definition of the insured event, the amount of coverage, the payment schedule, and the conditions for benefit payouts. A key provision is the incontestability clause, which limits the time period in which the insurance company can challenge the validity of the policy.
Understanding these clauses ensures clarity on the policy’s specifics.
Importance of Careful Review
Thorough review of the policy document is critical. This involves understanding the specific language used, identifying any ambiguities, and seeking clarification from the insurance company if necessary. A careful review helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures the policy aligns with the policyholder’s needs and expectations. This meticulous review is crucial to avoid any disputes or unforeseen issues later.
Structured Format for Understanding and Analyzing Policy Documents
A structured approach to reviewing policy documents can be highly beneficial. The following format provides a framework for understanding and analyzing the policy:
- Policy Summary: Start with a quick overview of the key features, such as coverage amount, premium payments, and benefit payouts.
- Definitions: Carefully review the definitions of key terms and conditions used in the policy. This ensures that all parties understand the exact meaning of the terms. For example, the policy might define the meaning of “death due to accident” or “terminal illness.”
- Premium Payment Schedule: Review the premium payment schedule and understand the consequences of missed payments. A clear understanding of the schedule ensures that the policy remains active.
- Benefit Payout Provisions: Thoroughly review the clauses relating to benefit payouts. This includes understanding the conditions under which the benefits are payable, the time frame for payout, and the payment method. Knowing the specifics helps avoid potential issues and ensures beneficiaries understand their rights.
- Exclusions and Limitations: Pay close attention to the exclusions and limitations of the policy. These clauses define the situations in which the policy does not provide coverage. Identifying exclusions prevents unnecessary claims or misunderstandings.
- Policy Amendments and Terminations: Understand the procedures for amending or terminating the policy. This includes the required documentation and the time frame for any changes. Having this knowledge is essential to understand the policy’s flexibility and potential for adjustments.
By following this structured approach, policyholders can gain a comprehensive understanding of their life insurance policies, facilitating informed decision-making and ensuring a smooth process for both policyholders and beneficiaries.
Life Insurance Claims Process

The process of claiming life insurance benefits can be complex and emotionally challenging for beneficiaries. Understanding the steps involved and the required documentation can significantly ease the process and ensure a smoother transition. This section details the procedures for filing a life insurance claim, the essential documentation, potential obstacles, and the typical timeframe.
Filing a Life Insurance Claim
A claim is initiated by notifying the insurance company of the insured’s death. This typically involves contacting the insurance company directly, following their specific claim procedures Artikeld in the policy documents. Prompt action is crucial to ensure a timely response and avoid potential delays.
Required Documentation
The insurance company will require specific documentation to validate the claim. This typically includes a certified death certificate, proof of the policy’s existence and validity, and the beneficiary’s identification and relationship to the deceased. Some insurance providers may also request additional documents, such as medical records or a police report, depending on the circumstances surrounding the death.
Claim Procedures
The insurance company will follow a defined procedure for processing the claim. This involves reviewing the submitted documentation, verifying the information, and conducting an investigation if needed. The investigation may include contacting witnesses, reviewing medical records, or conducting other relevant inquiries to ascertain the cause of death and confirm the policy’s validity. Verification of the beneficiary’s identity and eligibility is also a critical part of the procedure.
Potential Challenges and Complexities
Several factors can potentially complicate the claim process. Contesting the claim by other parties, discrepancies in the provided documentation, or a lack of clear evidence regarding the insured’s death can introduce delays. A thorough understanding of the policy’s terms and conditions, as well as a complete set of documentation, can mitigate potential challenges. Complex estates or situations with multiple beneficiaries can also lead to complications, requiring careful consideration of the policy terms.
Timeframe for Processing Life Insurance Claims
The timeframe for processing life insurance claims can vary depending on the insurance company, the complexity of the case, and the availability of required documentation. Generally, it can take several weeks to several months to complete the claim process. A streamlined process, coupled with the prompt submission of all required documents, will accelerate the claim resolution. Insurance companies typically provide an estimated timeframe for claim processing within their policies.
Flowchart of Claim Filing Steps
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Notify the insurance company of the death. |
| 2 | Gather necessary documentation (death certificate, policy details, beneficiary information). |
| 3 | Submit the claim form and supporting documents to the insurance company. |
| 4 | Insurance company reviews the claim and conducts an investigation (if necessary). |
| 5 | Settlement of the claim (if approved) and payment to the beneficiary. |
Life Insurance Options for Specific Needs
Life insurance isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Different life stages and individual circumstances necessitate tailored approaches. This section explores specific life insurance plans designed to address the unique needs of various groups, from young families to retirees. It also examines how life insurance can be strategically employed to address specific situations like critical illness or business succession.
Life Insurance for Young Families
Young families often face significant financial responsibilities, including raising children and potentially securing future education. Life insurance provides a safety net, ensuring financial security for dependents in the event of the primary breadwinner’s untimely demise. Term life insurance is frequently a practical choice for young families due to its affordability and flexibility. Permanent life insurance, like whole life, offers a long-term investment component, potentially growing wealth alongside the life insurance coverage.
Examples include term life insurance policies with increasing coverage amounts to match family needs and whole life policies that offer both death benefit and cash value accumulation.
Life Insurance for Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs often face unique challenges, including business succession and the need to protect their investment. Life insurance can play a crucial role in safeguarding business continuity and ensuring the smooth transition of ownership. Business owners may consider policies that offer significant death benefits to fund buy-out agreements or business continuation plans. Key person life insurance is a specific type of policy that covers the death of a crucial employee or executive who holds significant value to the business.
This protection allows for business continuity and potentially minimizes the disruption to the organization’s operations.
Life Insurance for Retirees
Retiring individuals might need life insurance to cover final expenses, ensure continued financial support for their spouse, or fund specific goals. Term life insurance tailored for retirees can provide coverage for a limited period, offering affordability and flexibility. In some cases, a combination of term and permanent life insurance might be considered, depending on the individual’s financial situation and future needs.
This approach offers a mix of short-term coverage for essential needs and potentially long-term benefits for investments.
Life Insurance for Critical Illness or Disability
Critical illness and disability insurance provide coverage for unforeseen health events that can significantly impact financial stability. These policies pay out benefits in the event of a critical illness diagnosis or a prolonged disability, providing a safety net for medical expenses, lost income, and other associated costs. The amount of coverage and the specific types of illnesses or disabilities covered can be tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
Consider the specific health concerns and potential financial burdens to choose the right policy.
Life Insurance for Business Succession Planning
Life insurance plays a vital role in ensuring business continuity during transitions. Business succession planning often involves buy-out agreements or funding for business operations in the event of a key individual’s death. Life insurance policies can provide the necessary funds to facilitate these arrangements. Business owners should assess their needs and involve legal counsel to develop a robust plan that addresses the financial implications of a transition.
Life Insurance Options Comparison Table
| Life Insurance Type | Suitable for | Key Features | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Term Life Insurance | Young families, individuals with short-term needs | Affordable, flexible coverage for a specific period | Funding education, covering mortgage, ensuring short-term financial security |
| Whole Life Insurance | Individuals seeking long-term coverage and cash value accumulation | Permanent coverage, cash value component, potential investment growth | Estate planning, long-term financial goals, wealth accumulation |
| Universal Life Insurance | Individuals with fluctuating needs, seeking flexibility in premiums | Flexible premiums, variable cash value component | Adapting to changing financial situations, achieving specific financial goals |
| Variable Life Insurance | Individuals seeking investment growth potential alongside coverage | Cash value component linked to investment options | Growing wealth, achieving long-term financial objectives |
| Business Owners Life Insurance | Entrepreneurs, business owners | Significant death benefits to fund buy-out agreements, business continuation | Ensuring business continuity, facilitating smooth ownership transitions |
| Critical Illness Insurance | Individuals seeking coverage for serious illnesses | Pays benefits upon diagnosis of a critical illness | Covering medical expenses, providing financial support |
Illustrative Examples of Life Insurance Scenarios
Life insurance isn’t just about protecting your loved ones; it’s a strategic tool for managing financial risks and securing your family’s future. Understanding how life insurance can function in various scenarios can help individuals make informed decisions about their coverage needs. This section provides practical examples to illustrate the value and application of life insurance.Illustrative examples showcase how life insurance can mitigate potential financial burdens and provide crucial support in times of need.
These scenarios highlight the various ways life insurance can be tailored to meet specific needs, from supporting young families to providing long-term financial security.
Family Financial Security Case Study
A young couple, Sarah and David, are starting a family. They have a mortgage, a growing child, and significant student loan debt. Without life insurance, Sarah’s sudden death could leave David struggling to manage the mortgage, child expenses, and loans. The financial burden could force them to sell assets, potentially leading to significant hardship for the family.
Life insurance, with a substantial death benefit, can cover these expenses, allowing David to maintain the family’s lifestyle and avoid a significant financial crisis.
Value of Life Insurance in Various Situations
Life insurance plays a critical role in numerous situations beyond simply covering a mortgage. Its application extends to various circumstances.
- Business Ownership: A sole proprietor’s death could lead to the business’s closure or sale, impacting the livelihood of employees and the owner’s family. Life insurance can provide funds to cover business debts, employee severance packages, and future operating expenses, ensuring a smooth transition and continuity.
- Education Funding: Life insurance can fund a child’s education. A substantial death benefit can cover tuition fees, living expenses, and other educational costs, allowing the child to pursue their academic aspirations without financial limitations.
- Estate Planning: Life insurance can be an integral part of estate planning. The death benefit can be used to cover estate taxes, debts, and other expenses, allowing for a more streamlined and efficient distribution of assets.
Hypothetical Scenarios Highlighting the Importance of Life Insurance
Life insurance offers significant protection in many hypothetical scenarios.
- Unexpected Illness: A parent’s unexpected illness or death could lead to substantial medical expenses and lost income. Life insurance can cover these expenses, preventing the family from accumulating further debt or jeopardizing their financial security.
- Caregiver Expenses: A parent providing long-term care for a child or elderly relative faces significant financial challenges. Life insurance can help cover the expenses associated with caregiving, ensuring that the caregiver’s needs are met without jeopardizing their financial well-being.
Mitigation of Financial Risks Through Life Insurance
Life insurance effectively mitigates potential financial risks. It provides a safety net, safeguarding against unexpected events and ensuring financial security for loved ones.
- Unexpected Death: Life insurance acts as a financial cushion in the event of an unexpected death. The death benefit can be used to cover funeral expenses, outstanding debts, and support the surviving family members.
- Disability: In the event of a disability, life insurance can provide a crucial income stream to help with medical expenses, lost wages, and other financial obligations.
Financial Outcomes with and without Life Insurance (Illustrative Table)
The following table illustrates the potential financial outcomes with and without life insurance in a hypothetical scenario.
| Scenario | Without Life Insurance | With Life Insurance (e.g., $500,000 Benefit) |
|---|---|---|
| Loss of primary income (death) | Family faces significant financial hardship; potential home loss, debt accumulation. | Funds available to cover mortgage, debts, and family expenses; financial stability maintained. |
| Education expenses | Limited or no funds for education; potential impact on children’s future opportunities. | Funds available to cover tuition, living expenses, and other educational needs. |
| Ongoing Expenses | Financial burden on surviving spouse/family members; difficulty in meeting daily expenses. | Financial security maintained; ability to meet ongoing expenses without financial strain. |
Potential Risks and Considerations of Life Insurance
Purchasing life insurance is a significant financial decision. While it offers crucial protection for loved ones, understanding potential drawbacks and risks is essential before committing. Careful consideration of various factors, including policy exclusions and limitations, is vital to making an informed choice.Careful evaluation of the policy’s terms and conditions, and an understanding of potential risks, is paramount before signing up for a life insurance policy.
This will allow you to make a well-informed decision, safeguarding your interests and those of your beneficiaries.
Policy Exclusions and Limitations
Understanding the specifics of a life insurance policy is crucial. Policies often have exclusions and limitations that may impact the coverage provided. These stipulations need careful review to ensure they align with your needs and expectations. Some policies may exclude specific pre-existing conditions or activities, or have limits on coverage for certain events. These exclusions can significantly reduce the overall benefit.
Policy Lapses or Non-Payment
Failure to meet payment obligations can lead to policy lapses. A lapsed policy will typically cease to provide coverage. This is a serious risk, as the financial protection offered by the policy is lost. It’s crucial to establish a budget and ensure consistent payment to avoid this outcome. Consider setting up automatic payments to minimize the risk of missed premiums.
Potential Issues Related to Policy Costs
Life insurance premiums can fluctuate based on various factors, such as age, health, and lifestyle choices. Understanding how these factors influence premium costs is essential. Increases in premiums can occur over time, potentially impacting the affordability of the policy. A thorough analysis of current and future financial situations is critical to ensure the policy remains financially manageable.
Factors to Consider Before Purchasing a Policy
Several factors need careful consideration before purchasing a life insurance policy. Evaluating your financial situation, family obligations, and long-term goals is important. These factors help determine the appropriate coverage amount and type of policy. Your current health status and lifestyle choices should also be taken into account, as they often influence premium rates. Consider consulting a financial advisor to gain a comprehensive understanding of these factors and to make an informed decision.
Table of Potential Risks and Considerations
| Risk Category | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Policy Exclusions | Specific circumstances or conditions not covered by the policy. | Thoroughly review policy wording; consider seeking professional advice. |
| Policy Lapses | Policy termination due to missed premium payments. | Establish a budget and utilize automatic payment options. |
| Premium Increases | Escalation in premiums over time. | Research policies with options for level premiums or consider policy riders. |
| Unforeseen Health Events | Unexpected health issues that might affect coverage or premium rates. | Consider policies with guaranteed insurability options or supplemental coverage. |
Last Word
In conclusion, life insurance plans offer crucial financial protection and peace of mind. Choosing the right plan involves careful consideration of individual circumstances and needs. Remember to consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance and to ensure the plan aligns with your long-term goals.
Common Queries
What are the different types of life insurance policies?
Common types include term life, whole life, and universal life insurance. Each type offers different coverage durations, cash value accumulation, and premium structures.
How does my health affect my life insurance premiums?
Your health status, including pre-existing conditions, plays a significant role in determining your premium. Policies assess risk based on health factors, which can result in higher premiums for those with known health issues.
What are the tax implications of life insurance?
Generally, life insurance premiums are not tax-deductible. However, death benefits are typically tax-free to beneficiaries.
How long does the life insurance claim process take?
The timeframe for processing life insurance claims varies depending on the insurer and the specifics of the claim. Thorough documentation and adherence to procedures can help expedite the process.
What is the difference between term and whole life insurance?
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific term, while whole life insurance provides coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured. Whole life also accumulates cash value, while term life does not.