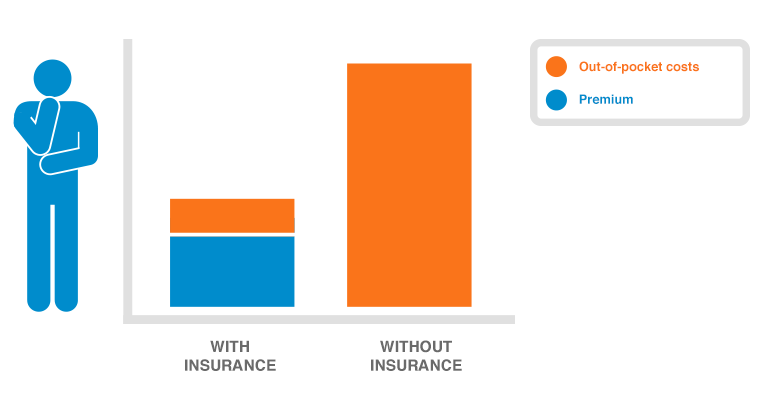
Navigating the complexities of health insurance costs can feel overwhelming. Premiums, deductibles, and co-pays can vary significantly, making it crucial to understand the factors influencing these costs. This guide dives deep into the world of health insurance, offering a clear and concise overview of everything from plan types to cost-saving strategies.
From understanding the different types of plans and their associated costs, to comparing in-network and out-of-network care, this resource provides a thorough exploration of health insurance cost structures. We’ll also examine trends and future outlooks, along with cost-saving strategies and helpful FAQs.
Understanding Health Insurance Costs

Health insurance premiums are influenced by a multitude of factors, impacting individuals and families differently. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about health insurance plans. Choosing the right plan requires careful consideration of personal needs and financial situations.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
Several key elements significantly impact the cost of health insurance. These include factors related to individual characteristics, healthcare utilization, and plan features.
- Individual Demographics: Age, location, and pre-existing health conditions are crucial factors in determining premiums. Generally, younger individuals and those without pre-existing conditions pay lower premiums, whereas older individuals and those with pre-existing conditions pay higher premiums.
- Healthcare Utilization: Past healthcare utilization, such as hospitalizations or doctor visits, can influence premiums. Individuals with a history of high healthcare utilization often face higher premiums due to the anticipated higher need for future care.
- Plan Features: The specific features of a health insurance plan, like the level of coverage, out-of-pocket maximums, and provider networks, directly affect premiums. Plans with broader coverage and extensive provider networks typically have higher premiums compared to plans with more limited features.
- Economic Factors: Overall economic conditions, including inflation and changes in the insurance market, also play a role in premium fluctuations. Market forces and government regulations can affect insurance costs, resulting in both increases and decreases.
Types of Health Insurance Plans and Cost Variations
Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and cost structures. Understanding the different plan types and their associated costs is essential for choosing the right plan.
- Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum plans: These plans are categorized by their cost-sharing levels, which impact the out-of-pocket expenses. Bronze plans have the lowest premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs, while Platinum plans have higher premiums but lower out-of-pocket costs. Silver and Gold plans fall between these two extremes in terms of premium and cost-sharing.
- Catastrophic plans: These plans offer minimal coverage for everyday medical needs and are generally very inexpensive, often designed for individuals who anticipate minimal need for medical services.
- High-deductible health plans (HDHPs): These plans have high deductibles but often lower premiums. They usually require significant out-of-pocket expenses before substantial coverage begins, making them suitable for those who anticipate managing their healthcare costs efficiently.
Demographic Impact on Insurance Costs
Demographics, including age, location, and family size, significantly affect health insurance premiums.
- Age: Generally, premiums increase with age due to the increased likelihood of needing healthcare services as individuals get older. Older individuals typically have higher medical costs and therefore, pay higher premiums.
- Location: Premiums can vary significantly based on location due to factors like healthcare costs, provider availability, and the prevalence of certain medical conditions in a given area. Areas with high healthcare costs will often have higher insurance premiums.
- Family Size: Adding family members to a health insurance plan usually results in higher premiums due to the increased risk of medical expenses associated with multiple individuals. The more individuals covered, the higher the cost of the plan.
Comparison of Health Insurance Plan Costs
The table below provides a simplified comparison of Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum plan costs. Actual costs vary widely based on individual factors and plan specifics.
| Plan Type | Premium (Estimated) | Cost-Sharing (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Bronze | $150/month | Higher out-of-pocket costs |
| Silver | $250/month | Moderate out-of-pocket costs |
| Gold | $350/month | Lower out-of-pocket costs |
| Platinum | $450/month | Lowest out-of-pocket costs |
Cost Comparison and Analysis
Understanding the different costs associated with health insurance is crucial for making informed decisions. This section delves into the factors influencing premiums, comparing in-network and out-of-network care, and analyzing the impact of pre-existing conditions. It also highlights the financial difference between preventive care and treatment.
Analyzing health insurance costs involves examining numerous variables. Premiums are influenced by a multitude of factors, from the specific benefits included to the geographic location of the policyholder. This analysis will provide a clearer picture of the complexities involved.
In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Care Costs
Choosing between in-network and out-of-network providers significantly impacts healthcare expenses. In-network providers have pre-negotiated rates with insurance companies, resulting in lower out-of-pocket costs for patients. Conversely, out-of-network care often necessitates higher deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance. This difference can lead to substantial financial burdens, especially for significant medical procedures.
Key Elements Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
Several factors influence the cost of health insurance premiums. Factors include age, location, chosen coverage level, and pre-existing conditions. Insurance companies use actuarial data to assess risk and set premiums accordingly. For example, individuals in high-risk areas may face higher premiums due to a higher likelihood of healthcare utilization. Moreover, individuals who opt for more extensive coverage, including preventive care and extensive hospital networks, often pay more.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions on Insurance Costs
Pre-existing conditions, such as chronic illnesses or prior surgeries, can affect health insurance premiums. Historically, insurers could deny coverage or impose higher premiums on individuals with pre-existing conditions. However, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the US, and similar legislation in other countries, has largely addressed this issue by mandating that insurers cannot exclude coverage or charge higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. While the ACA has made significant progress, variations in insurance policies still exist.
Preventive Care vs. Treatment Costs
Preventive care, such as vaccinations and regular check-ups, can help prevent costly illnesses and treatments in the future. A proactive approach to healthcare can significantly reduce long-term expenses. Treatment costs, on the other hand, vary widely depending on the severity and type of illness or injury. A comparison table below illustrates the potential difference in costs between preventive care and treatment.
| Category | Preventive Care | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Relatively low (e.g., annual check-up fees) | Potentially high (e.g., hospitalization, medication costs) |
| Long-Term Cost | Potentially lower (prevention of serious illness) | Potentially higher (management of chronic conditions, potential future complications) |
| Examples | Annual physical exams, vaccinations, screenings | Hospital stays, surgeries, medication prescriptions |
Cost-Saving Strategies
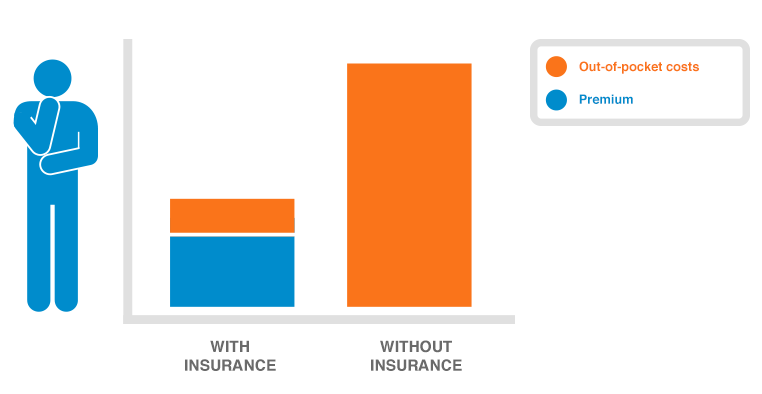
Health insurance premiums can be a significant financial burden. Understanding effective cost-saving strategies can significantly reduce the financial strain associated with healthcare. This section Artikels various methods to lower premiums, out-of-pocket expenses, and overall healthcare costs.
Effective strategies for managing health insurance costs encompass a multifaceted approach, considering individual needs and circumstances. This includes analyzing available plans, exploring negotiation tactics, and understanding the potential of high-deductible plans and health savings accounts (HSAs). By implementing these strategies, individuals and families can better control their healthcare spending.
Negotiating Lower Premiums
Negotiating lower health insurance premiums involves proactive communication and comparison. Researching different plans from various providers is crucial. Consider factors like plan benefits, network coverage, and provider options. Comparing plans side-by-side allows for a clear understanding of pricing and coverage differences. Utilize online comparison tools and consult with insurance brokers to gain a comprehensive understanding of available options. Some providers offer discounts for employees with clean health records or those who participate in wellness programs.
Benefits of High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) often feature lower premiums than traditional plans. The trade-off is a higher out-of-pocket expense for covered services until the deductible is met. This strategy can be beneficial for those with healthy lifestyles, expecting minimal healthcare utilization, and capable of handling substantial upfront costs. The potential for substantial savings on premiums can be a compelling factor in choosing an HDHP. Consider the potential for long-term savings and whether you can comfortably manage a higher deductible.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are tax-advantaged accounts that allow individuals enrolled in HDHPs to set aside pre-tax dollars for qualified medical expenses. These accounts offer a significant opportunity to reduce out-of-pocket costs. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and earnings within the account grow tax-free. Distributing funds towards covered medical expenses during the year helps reduce the financial burden of unexpected health issues.
Reducing Out-of-Pocket Healthcare Expenses
Managing out-of-pocket healthcare expenses involves a proactive approach to healthcare utilization. Preventive care, including regular checkups and screenings, can help identify potential health issues early. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through diet, exercise, and stress management can also minimize healthcare needs. Prioritize cost-effective healthcare providers and services within your insurance network to control expenses. Utilizing telehealth services for routine check-ups and minor medical concerns can be a more affordable option.
- Prioritize preventive care. Regular check-ups and screenings can detect health issues early, preventing more costly treatments later. For instance, routine mammograms can detect breast cancer in its early stages, significantly impacting treatment success and cost-effectiveness.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can contribute to a healthier lifestyle, reducing the likelihood of developing chronic illnesses and associated healthcare expenses.
- Compare healthcare providers and services. Choosing cost-effective providers and services within your insurance network can help control expenses. Carefully review the cost of procedures and treatments from various providers.
- Utilize telehealth services. Telehealth can provide convenient and often more affordable access to healthcare services, particularly for routine check-ups and minor medical concerns.
- Explore generic medications. Generic medications are often significantly cheaper than brand-name drugs and offer comparable efficacy. Consulting with your doctor about generic alternatives can lead to substantial savings.
- Negotiate prescription drug costs. Pharmacies and drug manufacturers may offer discounts or programs to reduce the cost of prescriptions. Exploring these options can significantly impact out-of-pocket expenses.
Trends and Future Outlook
Health insurance costs continue to be a significant concern for individuals and families worldwide. Understanding the factors driving these costs and anticipating future trends is crucial for informed decision-making. This section delves into recent cost increases, potential future impacts, the role of policy changes and technology, and international cost comparisons.
Recent Trends in Health Insurance Cost Increases
Rising healthcare costs are a major contributor to escalating premiums. Factors like increased utilization of advanced medical technologies, escalating pharmaceutical prices, and the rising cost of physician services all contribute to the overall increase. Furthermore, demographic shifts, including an aging population and a rise in chronic diseases, also play a significant role. These factors collectively contribute to the rising cost burden on health insurance providers.
Potential Future Impacts on Health Insurance Costs
Several factors suggest continued upward pressure on health insurance costs. Increased demand for specialized care, driven by advancements in medical technology, will likely contribute to future premium hikes. Moreover, the rising prevalence of chronic conditions, often requiring ongoing management and expensive treatments, will continue to impact the cost of care. Furthermore, the potential for unforeseen health crises or pandemics could have a significant impact on overall health insurance costs. The unpredictable nature of these events can significantly influence premiums and affordability.
Impact of Healthcare Policy Changes on Insurance Pricing
Healthcare policies play a substantial role in influencing health insurance costs. Government regulations and policies related to coverage, reimbursement rates for providers, and the overall structure of the healthcare system directly affect premiums. For instance, changes in reimbursement rates for medical procedures can alter the costs of health insurance plans, making some more expensive than others. Similarly, policy changes related to preventative care can also impact premiums, often leading to lower costs over time.
Role of Technology in Influencing Health Insurance Costs
Technological advancements have the potential to impact health insurance costs in both positive and negative ways. Telemedicine, for example, can lower costs by reducing the need for in-person visits. Data analytics and predictive modeling can help insurers better assess risk and manage costs. However, the implementation of new technologies may involve initial investments and potential integration challenges. Ultimately, the adoption of technology will be crucial in determining the long-term cost trends of health insurance.
Comparison of Health Insurance Costs in Different Countries
Health insurance costs vary significantly across different countries due to differing healthcare systems, regulations, and economic conditions. For instance, countries with universal healthcare systems, such as those in Europe, may have lower average premiums compared to countries with more privately funded systems. Factors like the extent of coverage, the role of government subsidies, and the average income levels of the population all influence the cost of health insurance across nations. A comparison of these factors across different countries offers a more complete understanding of the complexities surrounding health insurance costs.
Factors Affecting Health Insurance Costs
Understanding the complex interplay of factors influencing health insurance premiums is crucial for both consumers and providers. These factors range from the size and makeup of provider networks to the broader economic and regulatory landscape. Analyzing these elements helps illuminate the dynamic nature of health insurance costs.
The cost of health insurance is a multifaceted issue, shaped by a multitude of interrelated factors. From the providers you can access to the overall utilization of healthcare services, the forces driving premium fluctuations are intricate and require careful consideration.
Provider Networks and Insurance Costs
Provider networks play a significant role in determining health insurance costs. Networks encompassing a wide range of healthcare providers, including specialists, hospitals, and clinics, often lead to lower premiums. This is because patients have more options for care within their network, potentially leading to more cost-effective choices. Conversely, smaller or less comprehensive networks may result in higher premiums, as patients might face greater challenges in accessing preferred providers. The geographical area covered by the network and the concentration of providers within that area also impact costs.
Healthcare Utilization Patterns and Premiums
Healthcare utilization patterns directly influence premiums. Higher utilization rates, meaning more people seeking medical care and utilizing services, typically lead to higher premiums. This correlation arises from the increased demand for services and the associated cost burden on the insurance company. Factors such as the prevalence of chronic conditions within a population and the frequency of emergency room visits also influence utilization patterns and consequently, insurance premiums.
Medical Inflation and Insurance Costs
Medical inflation, the consistent increase in the prices of medical services and supplies, is a significant driver of health insurance costs. Rising costs for medications, procedures, and hospital stays directly translate into higher premiums. For instance, advancements in medical technology, while beneficial, can also contribute to medical inflation, as these advancements often come with increased costs for implementation and use. Examples of this can be seen in the rising costs of specialized treatments and diagnostic tools.
Government Regulations and Insurance Costs
Government regulations, such as mandates for coverage and reimbursement rates, can significantly impact health insurance costs. Regulations may dictate what services must be covered by insurers, potentially leading to higher premiums. The impact of these regulations varies across different states and countries, creating a complex regulatory landscape. The Affordable Care Act (ACA), for example, has had a profound effect on health insurance costs and coverage.
Market Forces and Health Insurance Pricing
Market forces, including competition and consumer demand, also play a role in shaping health insurance pricing. Competitive insurance markets, with multiple providers vying for customers, may result in lower premiums as companies strive to attract and retain clients. Conversely, limited competition in a particular market could lead to higher premiums due to a lack of pricing pressure. Demand for specific types of coverage and services also impacts insurance pricing.
Visual Representation of Data
Visual representations are crucial for understanding complex data like health insurance costs. Graphs, charts, and maps effectively convey trends, comparisons, and relationships, enabling easier comprehension and informed decision-making. These visuals allow us to quickly grasp patterns and anomalies, making it easier to identify cost drivers and potential savings.
Plan Cost Comparison
Visualizing the differences in health insurance plan costs is vital for consumers. A bar chart comparing premiums across various plans (e.g., Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum) would be effective. Each bar would represent a plan, with the height correlating to the annual premium. Color-coding plans based on coverage levels would enhance clarity. This allows consumers to immediately see the price differences and quickly compare coverage options. Different levels of coverage will correspond to different premium costs.
Trend of Health Insurance Costs
Visualizing the historical trend of health insurance costs provides valuable context. A line graph plotting the annual average premium over the past five years would be beneficial. The x-axis would represent the year, and the y-axis would represent the premium cost. This graph would show any upward or downward trends, highlighting periods of significant price fluctuations. This allows consumers to anticipate future price movements and adjust their financial plans accordingly.
Healthcare Utilization and Premiums
Understanding the relationship between healthcare utilization and premiums is essential. A scatter plot displaying the correlation between the average number of doctor visits per year and the premium cost per plan would effectively illustrate this relationship. This allows identification of potential cost drivers and provides insights into how utilization impacts premiums. This would show the correlation between healthcare use and insurance costs, revealing potential cost-saving strategies.
Regional Variations in Health Insurance Costs
A map highlighting regional variations in health insurance costs would be insightful. Each state or region could be color-coded based on the average premium cost. A heatmap style would highlight areas with significantly higher or lower costs, offering insight into geographical cost factors. This would provide a visual overview of geographic disparities in health insurance costs, prompting further investigation into specific regional drivers.
Factors Contributing to Health Insurance Costs (Infographic)
An infographic detailing the factors influencing health insurance costs would provide a comprehensive overview. The infographic would visually represent the interplay of factors like medical inflation, healthcare utilization, demographics, and government regulations. Each factor would be represented with icons or symbols, and arrows would show the direction of influence (e.g., an arrow pointing from medical inflation to premiums). This visual representation would aid in understanding the interconnectedness of various factors that contribute to health insurance costs. The infographic would clearly display the contribution of different factors to the overall health insurance cost, aiding in consumer understanding.
Understanding Coverage and Costs
Understanding the components of health insurance coverage is crucial for making informed decisions about your plan. Different plans offer varying levels of protection, and understanding the associated costs is essential to budgeting for healthcare expenses. This section delves into the specifics of deductibles, co-pays, co-insurance, coverage options, out-of-pocket maximums, and how different coverage levels impact overall costs.
Health insurance plans often use a combination of cost-sharing mechanisms to manage costs. These mechanisms, such as deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance, affect the overall out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare services. Understanding these elements allows you to accurately estimate the total cost of care under a specific plan.
Factors Affecting Deductibles, Co-pays, and Co-insurance
Deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance are crucial components of cost-sharing in health insurance plans. A deductible is the amount you pay for covered services before your insurance begins to pay. Co-pays are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, like doctor visits or prescription drugs. Co-insurance is a percentage of the cost of a covered service that you are responsible for paying after meeting your deductible. These factors vary significantly between plans and often influence the overall cost of care. For example, a plan with a high deductible may offer lower premiums but result in higher out-of-pocket costs during a period of illness.
Examples of Different Coverage Options and Their Associated Costs
Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage. A high-deductible health plan (HDHP) often has lower premiums but requires a substantial initial payment before insurance kicks in. These plans often come with a health savings account (HSA) option, which can help offset out-of-pocket costs. Conversely, a plan with a lower deductible and higher premiums may provide more comprehensive coverage with lower out-of-pocket costs. Examples include plans offering comprehensive coverage for routine checkups, preventive care, and specialist visits, which may include higher premiums but potentially lower overall out-of-pocket expenses.
Factors Determining Out-of-Pocket Maximums
The out-of-pocket maximum is the most you will pay for covered services in a given plan year. This limit protects you from excessive costs. Factors determining this maximum include the specific plan, the level of coverage, and the average costs of medical services in your area. The out-of-pocket maximum varies widely among different plans.
Different Types of Health Insurance Coverage Options
| Coverage Type | Description | Potential Costs |
|---|---|---|
| High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | Offers lower premiums with a higher deductible. | Lower premiums, higher out-of-pocket costs until deductible is met. |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | Allows you to see doctors outside the network, but with potentially higher costs. | Premiums may be higher, but out-of-pocket costs may be lower with in-network providers. |
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | Requires you to select a primary care physician who coordinates your care. | Premiums are often lower, but choosing out-of-network providers will have higher costs. |
The table above provides a simplified overview of different types of health insurance plans. Choosing the right plan depends on individual needs and financial situations.
How Different Levels of Coverage Affect the Total Cost
Different levels of coverage significantly affect the total cost of care. A plan with extensive coverage for various medical services will likely have higher premiums. Conversely, a plan with limited coverage might have lower premiums but result in higher out-of-pocket costs. This demonstrates the trade-off between premium costs and the amount you pay directly for medical services. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for making an informed decision.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding health insurance costs is vital for making informed decisions about your healthcare. This guide has explored the multifaceted nature of these costs, from the foundational factors influencing premiums to the practical strategies for saving money. By understanding the nuances of different plans, the impact of various factors, and the trends shaping the future, you’re better equipped to manage your healthcare expenses and secure a more financially sound future.
Clarifying Questions
What factors influence health insurance premiums?
Factors influencing health insurance premiums are numerous, including your age, location, health status, and the type of plan chosen. Provider networks, healthcare utilization patterns, and even medical inflation all play a role.
How do pre-existing conditions affect insurance costs?
Pre-existing conditions can impact insurance costs, sometimes leading to higher premiums or even exclusion from coverage. The specifics vary depending on the plan and the condition.
What are some strategies for lowering health insurance costs?
Strategies for lowering health insurance costs can include choosing a high-deductible plan, utilizing health savings accounts (HSAs), negotiating lower premiums, and taking advantage of preventive care options.
What is the difference between in-network and out-of-network care?
In-network care typically results in lower costs, as providers have agreed-upon fees with the insurance company. Out-of-network care often involves higher costs, as you’ll pay more for services.
How do deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance affect overall costs?
Deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance are crucial components of health insurance plans. Deductibles are the amount you pay out-of-pocket before insurance starts covering costs. Co-pays are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, while co-insurance is a percentage of the cost you pay for certain medical expenses.