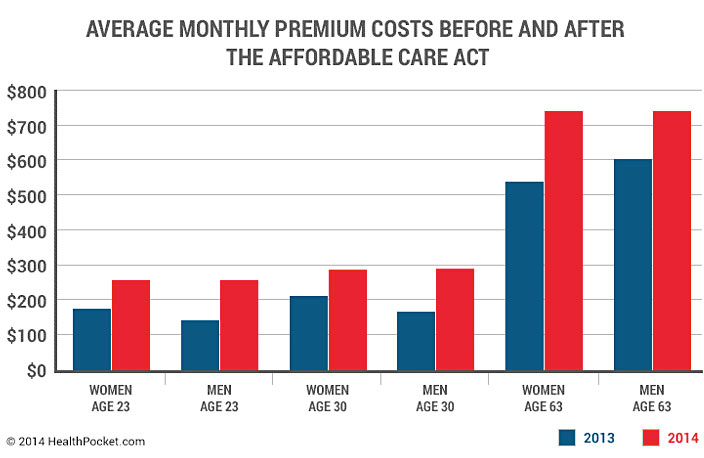
Understanding average health insurance costs is crucial for informed decision-making. This guide delves into the complexities of premiums, exploring factors influencing costs and strategies for saving money. From national variations to individual factors, we’ll dissect the intricacies of health insurance pricing.
This exploration covers a broad range of topics, from the influence of age and health status on premiums to the differences between various insurance plans. We also examine cost trends over time, highlighting key events and factors that have shaped the current landscape. Finally, we present practical strategies for consumers to reduce their insurance costs, enabling a more affordable healthcare experience.
National vs. Regional Cost Variations
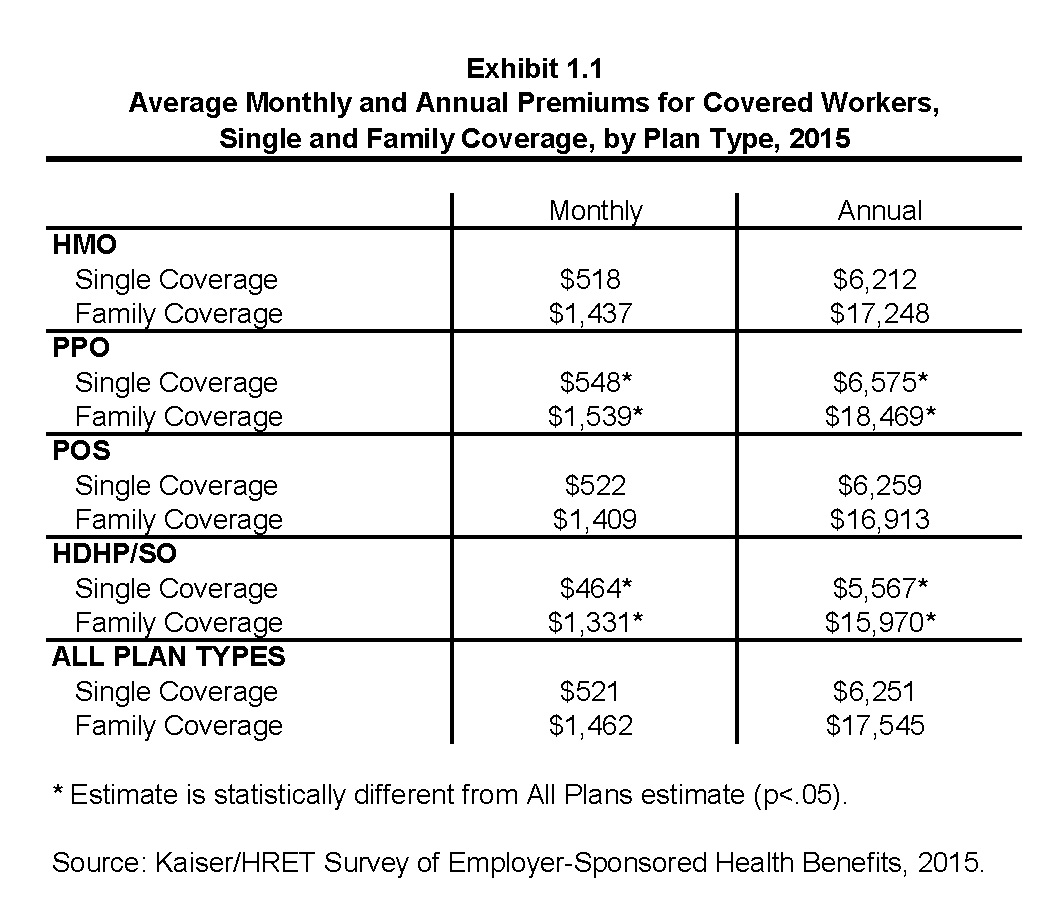
Health insurance premiums vary significantly across the United States, influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these regional disparities is crucial for individuals and families seeking coverage. These variations can lead to substantial differences in affordability and accessibility, impacting the overall health of communities.
Regional Cost Differences
Significant variations in health insurance costs exist between US states and regions. Factors such as healthcare infrastructure, population density, demographics, and state regulations play a critical role in shaping these disparities. The following table illustrates the range of average costs and associated contributing factors.
| State/Region | Average Cost | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| New England | $250-$350/month | Higher cost of living, specialized healthcare services, and relatively high population density. |
| Midwest | $200-$300/month | Generally lower cost of living compared to the coasts, but variations within the region exist based on specific factors like healthcare infrastructure and demographics. |
| South | $150-$250/month | Lower cost of living, but some areas may have lower access to specialized care, impacting costs indirectly. |
| West Coast | $280-$400/month | High cost of living, specialized healthcare services, and variations in population density across different regions within the West Coast. |
Factors Influencing Regional Costs
Several key factors contribute to the differences in health insurance premiums across US regions.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: The availability and quality of hospitals, doctors, and other healthcare providers in a region can influence costs. Areas with a strong healthcare infrastructure often have higher premiums due to higher demand and potentially greater service costs. For example, states with fewer hospitals or primary care physicians may have higher premiums to attract providers.
- Population Density: Regions with high population density tend to have higher healthcare utilization rates. Increased demand for services, like emergency room visits, may lead to higher premiums.
- Demographics: The age, health status, and prevalence of chronic diseases in a population directly affect the expected healthcare costs. Areas with a higher proportion of elderly individuals or individuals with pre-existing conditions may see higher premiums.
- State Regulations: State-level regulations on insurance markets, including mandates for coverage and regulations on premium levels, can influence the overall cost of health insurance.
- Cost of Living: Higher costs of living often correlate with higher health insurance premiums. This is because healthcare providers and insurance companies factor in the overall cost of operation within the region.
Impact of Regional Variations
The wide range of health insurance costs across the US can have a significant impact on individuals and communities. Lower premiums in some regions can increase access to care, leading to better health outcomes. Conversely, higher premiums in other areas can limit access to essential services.
Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, making it challenging to predict exact costs. Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals and families seeking to manage their healthcare expenses effectively. The premiums reflect the risk insurers take in providing coverage, and these risks are often correlated to demographics, lifestyle, and medical history.
Age
Age is a significant determinant of health insurance premiums. Generally, premiums tend to increase with age. Younger individuals are perceived as lower risk due to their generally healthier physiological state, while older individuals are often considered higher risk, given the possibility of more prevalent chronic conditions. This age-related risk assessment directly impacts premium costs. For instance, a 25-year-old with no pre-existing conditions will likely pay significantly less than a 65-year-old with a history of heart disease.
Health Status
The health status of an individual is a primary factor affecting premiums. Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or cancer, usually face higher premiums. Insurers assess the risk associated with these conditions, reflecting the potential for increased healthcare costs over the insured period. This risk assessment is crucial for setting premiums that are both equitable for all policyholders and sustainable for the insurance company. For example, an individual with a history of severe asthma will likely pay more than someone without respiratory issues.
Location
Geographical location significantly influences insurance premiums. Areas with higher healthcare costs, such as metropolitan areas or regions with a higher concentration of specialists, tend to have higher premiums. The cost of healthcare services, including hospital stays, specialist visits, and medications, is often factored into the premiums charged in specific areas. In regions with lower healthcare accessibility, premiums might be lower. For example, insurance premiums in a coastal city with renowned hospitals and specialists will likely be higher than in a rural area with fewer healthcare facilities.
Family Size
Family size also plays a role in determining insurance premiums. Larger families typically face higher premiums due to the increased risk of potential healthcare needs. Insurers consider the probability of multiple individuals needing care concurrently, which impacts the overall financial burden. For example, a family with four children will likely pay more than a single-person household, due to the higher chance of medical needs across multiple members.
Coverage Choices
The specific coverage options selected can impact premium costs. More comprehensive plans with wider coverage tend to have higher premiums than plans with limited coverage. Factors such as deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums influence the overall cost. A plan with a higher deductible might have a lower premium but will require a larger out-of-pocket expense in case of a claim. Individuals should carefully evaluate their needs and preferences when selecting a plan to manage their premium costs.
Interaction of Factors
The factors mentioned above interact in complex ways to determine the overall cost of health insurance premiums. For instance, an older individual living in a high-cost area with a pre-existing condition and a large family will likely pay significantly more than a younger, healthy individual living in a lower-cost area. Understanding how these factors work together is vital for making informed decisions about health insurance coverage.
Types of Health Insurance Plans and Their Costs
Health insurance plans vary significantly in their features and costs, impacting individuals’ financial and healthcare access. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions. Choosing the right plan depends on individual needs and budget constraints.
Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage and out-of-pocket expenses. These plans often fall into categories like HMOs, PPOs, and EPOs, each with its own set of characteristics that affect premiums.
Comparison of Health Insurance Plan Types
Various health insurance plan types cater to different healthcare needs and budgets. Understanding the key distinctions between these plan types can help individuals select the most suitable option for their circumstances. This comparison provides a general overview, and specific features and costs can vary based on the insurance provider and location.
| Plan Type | Average Cost (Estimated) | Covered Services | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | Generally lower than PPOs | In-network doctors, hospitals, and specialists. Preventive care often included. | Requires a primary care physician (PCP) referral for specialist visits. High level of cost control, often resulting in lower premiums. |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | Generally higher than HMOs | Wider network of doctors, hospitals, and specialists. Out-of-network care is available, but at a higher cost. | Allows greater flexibility in choosing providers, but out-of-network costs are usually higher. Typically offers more options for specialists and hospitals. |
| Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) | Generally in the middle | In-network doctors, hospitals, and specialists. Preventive care usually included. | Requires choosing a PCP and sometimes specialists, but allows some out-of-network care without a referral. Provides more flexibility than HMOs but less than PPOs. |
Factors Influencing Plan Costs
Several factors contribute to the variation in health insurance premiums. Understanding these elements can help individuals budget effectively for healthcare expenses.
- Geographic Location: Health insurance costs often vary significantly by region, influenced by factors like healthcare availability and demand. Areas with higher medical costs tend to have higher premiums.
- Age: Age is a significant factor in determining insurance premiums. Younger individuals typically pay lower premiums than older individuals due to the lower likelihood of significant medical expenses.
- Coverage: The breadth of covered services, including preventive care, prescription drugs, and mental health, impacts premiums. Comprehensive coverage often leads to higher premiums compared to plans with limited coverage.
- Plan Deductibles: The amount an individual must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company starts covering expenses directly affects the premium. Higher deductibles generally result in lower premiums.
Examples of Plan Features Impacting Cost
Specific plan features directly correlate with the overall cost. These elements help individuals understand how plan choices affect their financial responsibilities.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: Plans with robust prescription drug coverage often have higher premiums. Individuals who rely heavily on prescription medications need to consider this factor carefully when selecting a plan.
- Preventive Care: Plans that include comprehensive preventive care, such as routine checkups and vaccinations, typically have lower premiums, as preventive care often reduces the likelihood of more significant medical issues in the future.
- Out-of-Network Costs: Plans with lower out-of-network costs will likely have higher premiums, reflecting the broader network of providers covered.
Trends in Health Insurance Costs Over Time
Health insurance costs have fluctuated significantly over the past two decades, influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors, healthcare advancements, and policy changes. Understanding these trends is crucial for individuals and businesses seeking to navigate the evolving landscape of health insurance.
Historical Overview of Average Costs
The following table presents a snapshot of average health insurance costs over the past two decades, alongside key events that influenced the trends. Data sources for average costs may vary depending on the specific dataset. It is important to remember that these are averages and individual costs can vary considerably.
| Year | Average Cost (USD) | Influencing Events |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | $8,000 | Economic downturn, increasing prescription drug costs. |
| 2008 | $9,500 | The Great Recession, rising healthcare costs. |
| 2010 | $10,200 | Affordable Care Act (ACA) implementation, mixed effects on costs. |
| 2012 | $11,500 | Increased demand for healthcare services, insurance market adjustments. |
| 2015 | $12,800 | Technological advancements in healthcare, rising administrative costs. |
| 2018 | $14,200 | Changes in medical care delivery models, inflation, drug price increases. |
| 2020 | $15,500 | COVID-19 pandemic, increased demand for hospital care, disruptions to supply chains. |
| 2022 | $17,000 | Post-pandemic recovery, persistent inflation, and rising costs of certain treatments. |
| 2023 | $17,800 | Inflationary pressures, persistent supply chain challenges, and evolving healthcare needs. |
Factors Driving Cost Changes
Several factors have driven the observed fluctuations in health insurance costs. These include:
- Technological Advancements: Medical innovations, while beneficial for patient care, often lead to higher costs due to the expense of research and development, and the integration of new technologies into healthcare facilities. For instance, the introduction of new imaging techniques or advanced surgical procedures can increase the price of care.
- Increased Use of Healthcare Services: Improved public awareness about health and preventative care, along with the availability of affordable health insurance, has led to a rise in preventative checkups and other healthcare utilization. This greater demand for services can inflate the cost of premiums for all policyholders.
- Inflationary Pressures: General inflation impacts all sectors, including healthcare. As the cost of labor, supplies, and other operational expenses rise, healthcare providers often pass these increases on to consumers through higher prices for services and premiums.
- Policy Changes and Regulations: Changes in government regulations and policies, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), can impact insurance costs in both positive and negative ways, sometimes creating market volatility and leading to changes in cost trends.
- Economic Conditions: Economic downturns or periods of uncertainty often affect healthcare spending. During recessions, individuals may delay or forgo non-essential medical procedures, while economic prosperity may increase healthcare utilization and thus drive up premiums.
Cost-Saving Strategies for Consumers
Reducing health insurance premiums requires proactive steps and informed choices. Consumers can significantly lower their costs by implementing various strategies, from making healthy lifestyle choices to actively participating in wellness programs. Understanding these options allows individuals to make financially savvy decisions that align with their health goals.
Preventative Care
Preventative care is a cornerstone of cost-effective healthcare. By prioritizing routine checkups and screenings, individuals can catch potential health issues early, potentially avoiding more expensive treatments later. This proactive approach can lead to lower overall healthcare costs.
- Regular checkups and screenings: Scheduling routine doctor visits and necessary screenings, such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and blood tests, is crucial. Early detection of health issues often translates to more affordable treatment options.
- Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date on vaccinations helps prevent illnesses that can lead to costly hospitalizations or long-term care.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity are key to preventing chronic diseases. These habits contribute to lower healthcare costs over time.
Wellness Programs
Many health insurance providers offer wellness programs that incentivize healthy behaviors. Participating in these programs can lead to significant savings on premiums. The advantages of such programs include improved health and financial benefits.
- Health assessments: These assessments help individuals understand their current health status and identify areas for improvement. Results provide tailored recommendations for a healthier lifestyle.
- Fitness challenges: Participating in fitness challenges, whether individual or group-based, encourages physical activity and healthy habits.
- Health coaching: Working with a health coach provides personalized guidance and support to help individuals achieve their health goals.
- Rewards programs: Many wellness programs offer rewards for achieving health milestones. These could include discounts on premiums, gift cards, or other incentives.
Health Insurance Plan Selection
Choosing the right health insurance plan is essential for controlling costs. Understanding plan features and coverage options helps individuals select the most suitable plan for their needs.
- Consider your health needs: Assess your current health status and anticipated healthcare needs. Select a plan that aligns with your specific requirements.
- Compare different plans: Analyze various plans to compare premiums, deductibles, and coverage options.
- Evaluate plan benefits: Look for plans that offer preventive care services and wellness programs.
Negotiating and Shopping
Consumers can potentially lower costs by negotiating with healthcare providers or utilizing online tools for comparing plans. These methods offer valuable opportunities for finding more affordable options.
- Negotiate with providers: Negotiating with providers for lower costs for specific procedures or services may be possible, especially for higher-cost procedures.
- Compare insurance plans online: Using online comparison tools allows for a comprehensive view of different plans and helps identify the most cost-effective options.
Medication Management
Managing prescription medications effectively can significantly impact healthcare costs. This involves strategic planning and adherence to doctor’s recommendations.
- Generic medications: Choosing generic medications instead of brand-name alternatives often results in substantial savings.
- Medication adherence: Adhering to prescribed medication regimens reduces the risk of health complications and associated costs.
- Consult with a pharmacist: Consulting a pharmacist for guidance on managing medications and potential cost-saving strategies is beneficial.
Health Insurance Costs by Age Group
Health insurance premiums often vary significantly across different age groups. This disparity is influenced by a multitude of factors, including the likelihood of developing health conditions and the associated healthcare needs. Understanding these variations is crucial for individuals and families planning their budgets and healthcare strategies.
Age is a key determinant in health insurance costs. Younger individuals, generally, have lower healthcare needs compared to older demographics. However, this is not always the case. Factors like pre-existing conditions or lifestyle choices can significantly impact costs at any age. This section will delve into the typical cost variations across age groups and the underlying reasons behind them.
Average health insurance costs can vary significantly, depending on factors like location and coverage. For example, if you’re looking at options like FEP Blue Dental, fep blue dental , you’ll need to check their specific rates to see how they fit within your budget. Ultimately, comparing various plans and their costs is key to finding the best deal.
Average Health Insurance Costs by Age Group
Insurance companies assess risk when setting premiums. Higher perceived risk leads to higher premiums. Age is a major risk factor. Different age groups exhibit varying health risks and healthcare needs, leading to discrepancies in premiums. The following table illustrates the general trends in health insurance costs across different age brackets.
Average health insurance costs can vary significantly, depending on factors like location and the specific health insurance policy chosen. Different plans offer varying levels of coverage, impacting the overall price. Ultimately, understanding the details of a policy is key to determining the actual cost.
| Age Group | Estimated Average Annual Premium (USD) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Young Adults (18-25) | $3,000 – $4,000 | Generally lower premiums due to lower likelihood of chronic conditions and preventative healthcare needs. |
| Middle-Aged Adults (26-54) | $4,000 – $6,000 | Premiums increase as individuals enter a phase where some may develop chronic conditions and need more frequent care. Preventive care needs also may increase. |
| Seniors (55+) | $6,000 – $8,000+ | Premiums increase considerably for seniors due to a higher prevalence of chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis, along with the associated costs of treatment and care. |
Reasons for Cost Variations
Several factors contribute to the variations in health insurance costs across age groups. These factors can include a combination of expected and unexpected factors.
Average health insurance costs can vary significantly, depending on factors like your location and coverage. However, if you’re planning a trip, consider getting travel insurance, like bcaa travel insurance , which often includes health coverage while you’re away. This can help offset some of the financial burden associated with unexpected medical expenses during your travels. It’s worth noting that these policies often have limits, and it’s good to compare them with your regular health insurance.
- Prevalence of Chronic Conditions: The risk of developing chronic conditions increases with age. This is a major reason for the rise in premiums for seniors. Conditions like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes are more prevalent in older age groups, leading to increased healthcare utilization and costs.
- Healthcare Utilization: Older individuals frequently require more specialized care and have higher healthcare utilization rates. This translates to higher premiums for insurance companies. Examples include visits to specialists, hospitalization, and prescription medications.
- Risk Factors and Lifestyle Choices: Lifestyle choices such as smoking, diet, and exercise can impact health risks at any age, influencing premiums. However, these factors often have more significant impacts on the long-term health and costs of individuals as they age.
- Medical Conditions and Pre-existing Conditions: Pre-existing conditions and other health conditions significantly influence premiums for all age groups. Individuals with pre-existing conditions may pay higher premiums, regardless of age. It is important to consider how these conditions may impact the long-term health and healthcare costs for an individual.
Impact of Health Conditions and Risk Factors
Health conditions and risk factors have a substantial impact on the costs of health insurance across all age groups. Insurance companies use these factors to assess the risk of future healthcare needs for an individual. The combination of these factors, in conjunction with other health-related considerations, helps to illustrate the varied costs and expectations.
Cost Comparison of Different Coverage Levels
Choosing the right health insurance coverage level is crucial for managing healthcare costs. Understanding the differences in benefits and out-of-pocket expenses associated with various plans helps consumers make informed decisions. This section provides a comparative analysis of different coverage tiers, highlighting their features and potential financial implications.
Coverage Level Descriptions
Different health insurance plans offer varying degrees of coverage, typically categorized as Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. These tiers reflect the level of risk sharing between the insurer and the insured. The higher the tier, the greater the insurer’s share of medical expenses.
Plan Features and Benefits
- Bronze plans offer the lowest premiums, reflecting a lower level of coverage. Generally, these plans have higher out-of-pocket expenses for covered services. They are best suited for individuals who anticipate minimal healthcare needs.
- Silver plans strike a balance between premium cost and coverage. They provide a moderate level of coverage, and the associated out-of-pocket expenses fall somewhere between Bronze and Gold plans.
- Gold plans provide a higher level of coverage compared to Silver and Bronze plans. Premiums are generally higher, but they offer more comprehensive benefits and lower out-of-pocket expenses. Individuals with higher healthcare needs often find Gold plans more advantageous.
- Platinum plans offer the highest level of coverage and the highest premiums. These plans typically have the lowest out-of-pocket expenses for covered services. They are suitable for those anticipating frequent or substantial healthcare utilization.
Cost Comparison Table
| Coverage Level | Average Premium (Example) | Deductible (Example) | Co-pay (Example) | Co-insurance (Example) | Out-of-Pocket Maximum (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bronze | $150/month | $2,000 | $25 | 80/20 | $6,000 |
| Silver | $250/month | $1,500 | $30 | 70/30 | $4,500 |
| Gold | $350/month | $1,000 | $20 | 50/50 | $3,000 |
| Platinum | $500/month | $500 | $15 | 20/80 | $2,000 |
Note: Premiums and cost-sharing amounts are examples and may vary significantly depending on location, provider, and individual circumstances.
Impact on Out-of-Pocket Expenses
The level of coverage directly impacts out-of-pocket expenses. Bronze plans typically result in higher out-of-pocket costs, while Platinum plans usually have the lowest out-of-pocket maximums.
Understanding the potential out-of-pocket expenses associated with each coverage level is vital for budgeting. For example, a person anticipating significant medical expenses might benefit from a higher-tier plan, even if it comes with a higher premium.
The Role of Employer-Sponsored Plans
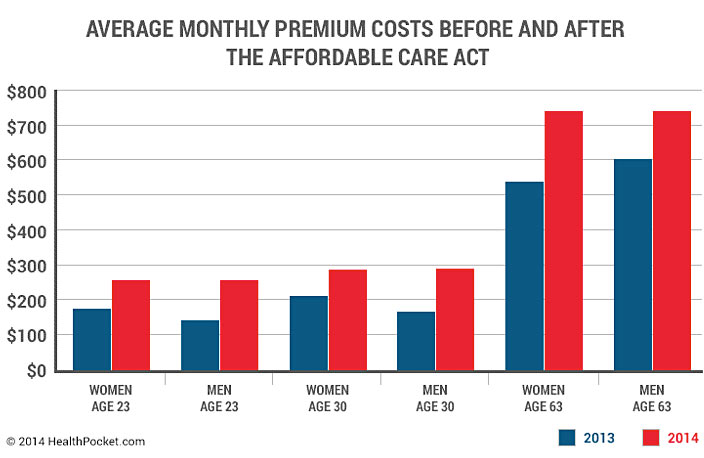
Employer-sponsored health insurance plans remain a dominant force in the US healthcare system, significantly influencing average healthcare costs. These plans, often offering comprehensive coverage, are a crucial factor in employees’ access to affordable healthcare. Their impact on overall costs extends beyond individual premiums, impacting healthcare utilization patterns and influencing the market as a whole.
Employer contributions play a pivotal role in determining the premiums employees pay. The level of employer contribution varies widely depending on factors like the size and financial health of the company, the type of industry, and the specific plan chosen. This contribution often reduces the financial burden on employees, making health insurance more accessible and potentially influencing their healthcare decisions.
Employer Contribution and Employee Premiums
Employer-sponsored plans typically involve a shared cost-splitting arrangement between the employer and employee. The employer’s contribution directly impacts the premium amount employees pay. A larger employer contribution reduces the employee’s share, making the plan more affordable. Conversely, a smaller employer contribution necessitates a higher employee premium. For example, a company might contribute 80% of the premium cost, leaving the employee responsible for 20%. This arrangement can be a significant factor in employee satisfaction and retention.
Plan Variations and Cost Implications
Employer-sponsored plans offer a variety of options, each with its own cost implications. High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) typically have lower monthly premiums but require employees to pay more out-of-pocket for covered services until their deductible is met. These plans often pair with health savings accounts (HSAs) to help employees manage these out-of-pocket costs. Conversely, plans with higher premiums may offer more comprehensive coverage and lower out-of-pocket expenses. Choosing the right plan involves balancing the cost of premiums with the level of coverage needed.
Impact of Employer Size and Industry
Employer size and industry have a considerable influence on plan costs. Larger companies often have more resources to negotiate lower premiums with insurance providers. Smaller companies may find that plan costs are proportionally higher due to reduced bargaining power. Similarly, industries with higher healthcare costs, like healthcare or hospitality, often face higher premiums compared to industries with lower healthcare needs. For example, a large technology company might be able to secure a more favorable plan compared to a small retail business. The industry’s risk profile is a major determinant.
Examples of Employer-Sponsored Plan Variations
| Plan Type | Description | Cost Implications |
|---|---|---|
| High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | Lower monthly premiums, higher out-of-pocket costs until the deductible is met. | Potentially lower overall cost but requires careful management of out-of-pocket expenses. |
| PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) | Wider network of healthcare providers, typically with higher premiums. | Greater flexibility in choosing providers, but potential higher costs than HMO plans. |
| HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) | More limited provider network, often with lower premiums. | Greater control over costs but may require using in-network providers. |
A company’s choice of plan significantly affects employee costs and healthcare access.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, average health insurance costs are influenced by a multitude of interacting factors, ranging from regional disparities to individual circumstances. This comprehensive overview has provided valuable insights into the complexities of healthcare costs. By understanding these nuances, consumers can make more informed decisions about their coverage and potentially reduce their out-of-pocket expenses. The information presented here offers a framework for navigating the health insurance market effectively.
Query Resolution
What factors influence the cost of health insurance in a specific region?
Factors like healthcare infrastructure, population density, and demographics play a significant role in regional cost variations. A region with advanced medical facilities might have higher costs compared to a region with fewer resources.
How do different health insurance plan types affect the cost?
The type of plan, such as HMO, PPO, or EPO, directly impacts the cost. HMO plans, often having lower premiums, typically limit the choice of healthcare providers, while PPO plans offer more flexibility, usually at a higher premium.
Are there ways to reduce health insurance premiums?
Yes, several strategies can lower premiums, including maintaining good health, enrolling in wellness programs, and exploring preventative care options. These proactive steps can often lead to lower costs in the long run.
How do employer-sponsored plans affect employee costs?
Employer-sponsored plans significantly impact employee costs. The extent of employer contributions directly affects the premiums paid by employees. Larger companies often offer more comprehensive plans with lower employee costs.